Flash
The goal is to save and load user configurations for application. Writting from the back of the flash memory.
Porting to different hardware requires user to edit Flash.hpp and Flash.cpp
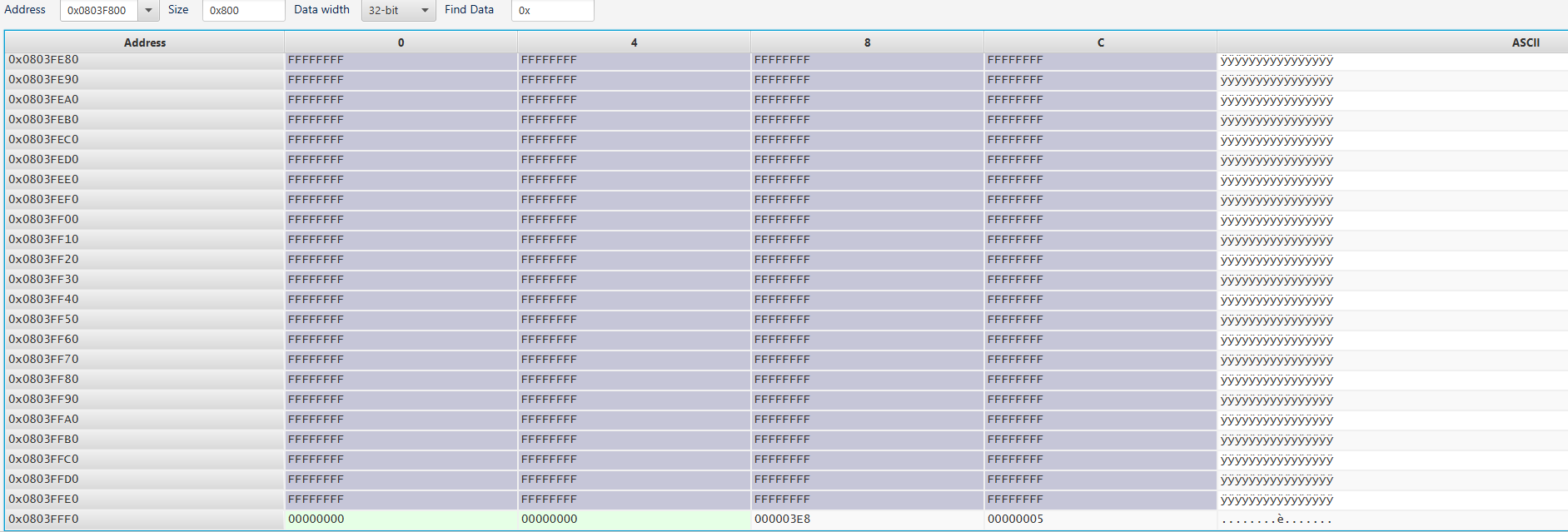
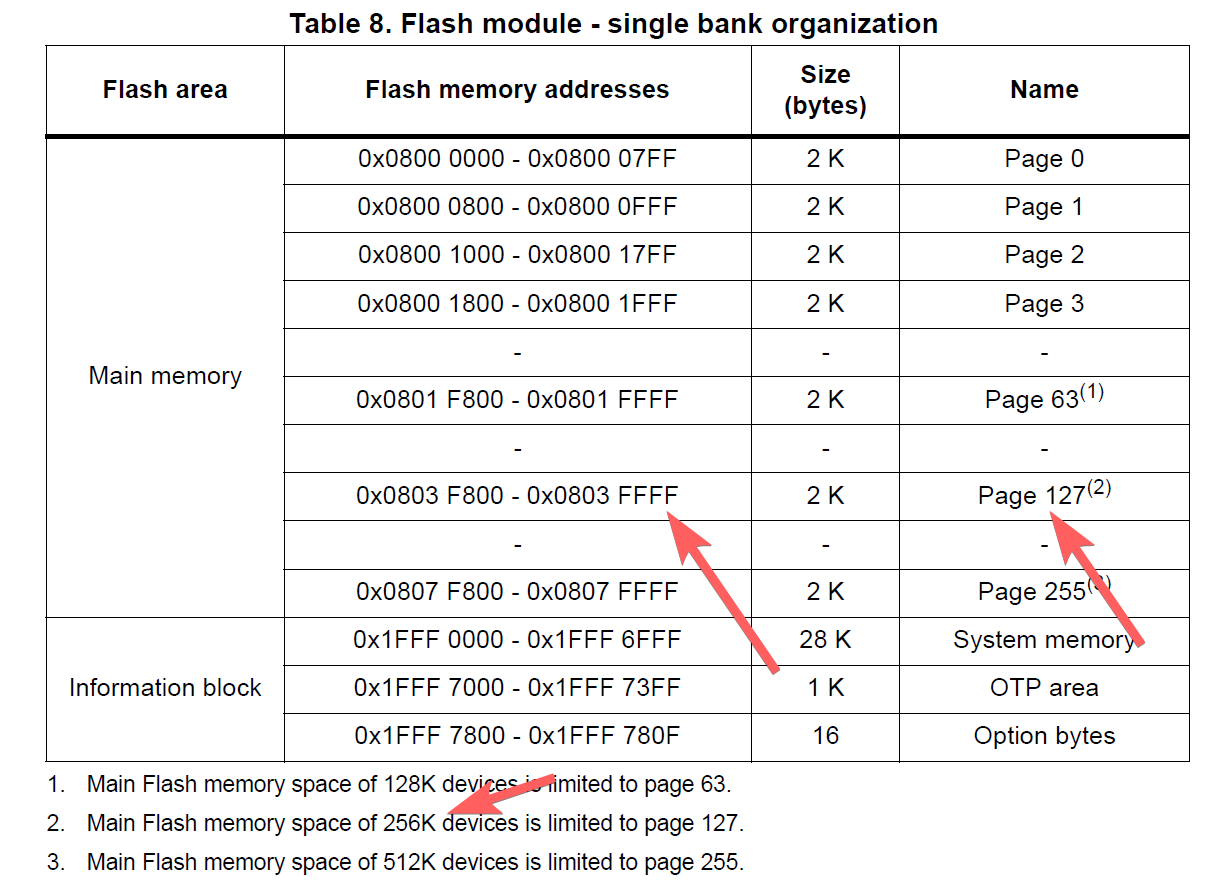
Refer to the Reference Manual and find out the end of flash address. Then, update those two variable.
// G432KB has 128Kb of flash
// Same as (0x0803FFFF + 1 - 0x8); if using datasheet provided value
const uint32_t m_address_end{0x08040000 - 0x8};
const uint8_t m_page_total{127};
The configuration data are packaged into a struct and union aligned to uint64_t array for double word HAL flash writing function. The pack and unpack is done manually by user.
You will need to edit this section to fit your application needs.
// Edit config_arr_size and Config content.
#define config_arr_size 2
union Config_Arr {
struct Config {
uint32_t led_level;
uint32_t led_scale;
} config;
uint64_t config_arr[config_arr_size];
};
In the public function Save() and Load(), you will need to manually pack and unpack your configuration to/from each of your instances.
Then, you will call the private function Write() and Read() to do flash access.
Below example saves and loads two configuration from LED usage.
void Flash::Save() {
Flash::Config_Arr current_config{};
current_config.config.led_level = led_user.getLevel();
current_config.config.led_scale = led_user.getScale();
Write(current_config.config_arr, config_arr_size);
}
void Flash::Load() {
Flash::Config_Arr loaded_config{};
Read(&loaded_config, config_arr_size);
led_user.setLevel(loaded_config.config.led_level);
led_user.setScale(loaded_config.config.led_scale);
}
The memory save example: